Record Sonar scan results in Kosli #
The results of SonarQube Server and SonarQube Cloud scans can be tracked in Kosli trails.
This integration involves setting up a Sonar webhook in Kosli and a corresponding webhook in SonarQube. When you run a scan of your SonarQube project, the webhook is triggered and the results of the scan are sent to Kosli.
Some parameters must be passed to the Sonar scanner when it is run (e.g. the name of the Flow corresponding to the project, and the name of the trail the results should be attested to); these are sent with the scan results, and allow Kosli to determine the compliance status of the results and attest them to the correct trail/artifact.
Setting up in Kosli #
To set up the integration, navigate to the Sonar integration page for your org in the Kosli app.
After switching on the integration, you will be provided with a webhook and a secret.
Configuring the flow name #
By default, Kosli will use the key of your SonarQube project as the flow name for the sonar attestation. You can configure this flow name in the "Flow Name Options" section on the integration page, by choosing either the project name or key as the base of the flow name, and then optionally adding a prefix and/or suffix.
Note that if you set the flow name by sending a parameter to the Sonar Scanner (see Scanner parameters below), this configuration will be overridden.
Setting up Sonar Webhooks #
You're now just a few steps away from connecting SonarQube to Kosli.
Both SonarQube Server and SonarQube Cloud provide two types of webhooks: global (which are triggered when any project in your organization is scanned) and project-specific (which are triggered by a scan for that project only). Kosli supports both types of webhooks.
In SonarQube Cloud or SonarQube Server:
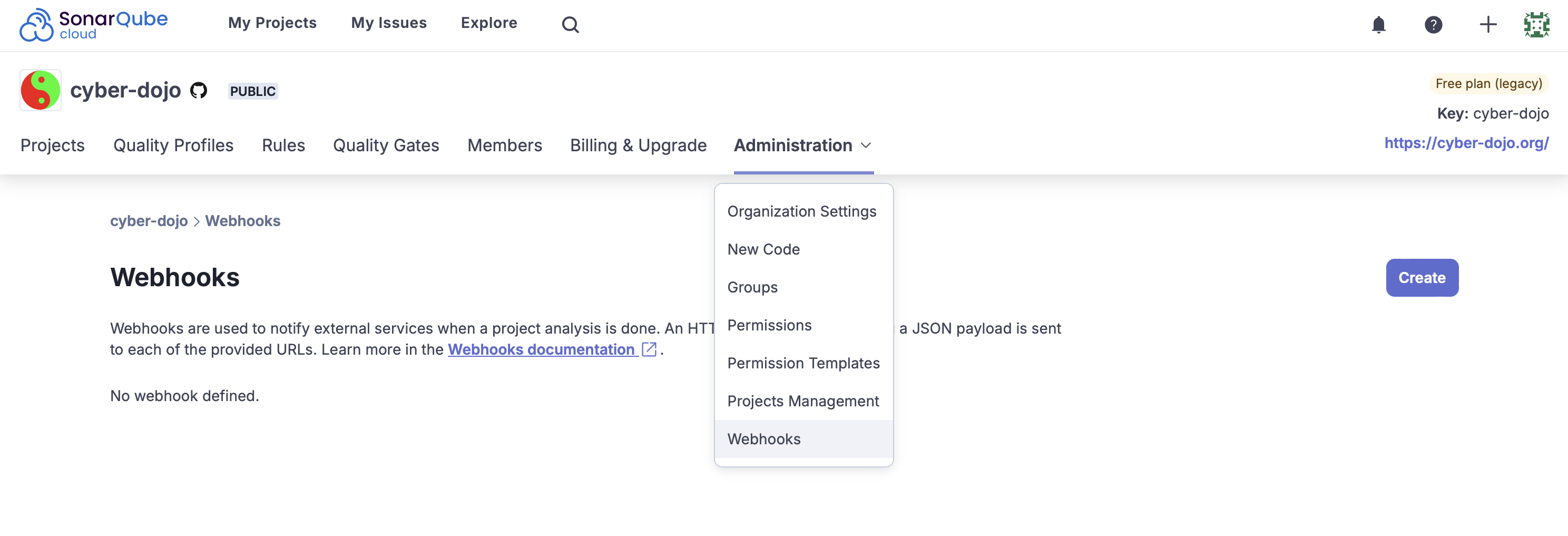
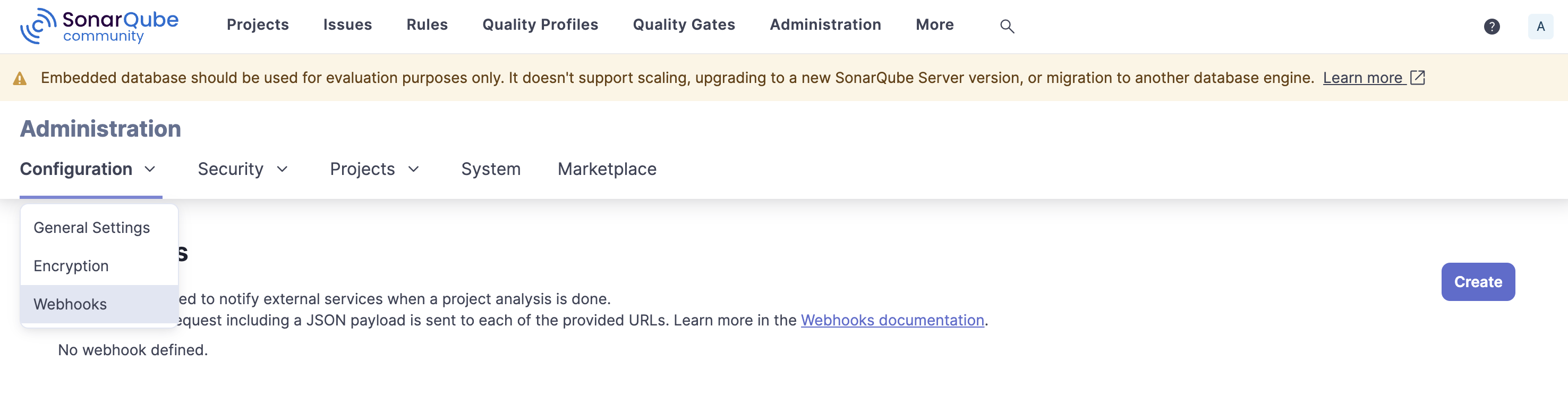
To create a global webhook: #
- In SonarQube Cloud: Go to your Organization, then Administration > Webhooks
- In SonarQube Server: Go to Administration > Configuration > Webhooks
- Create a new Webhook
- Add the Kosli webhook URL and secret provided
- Click Create
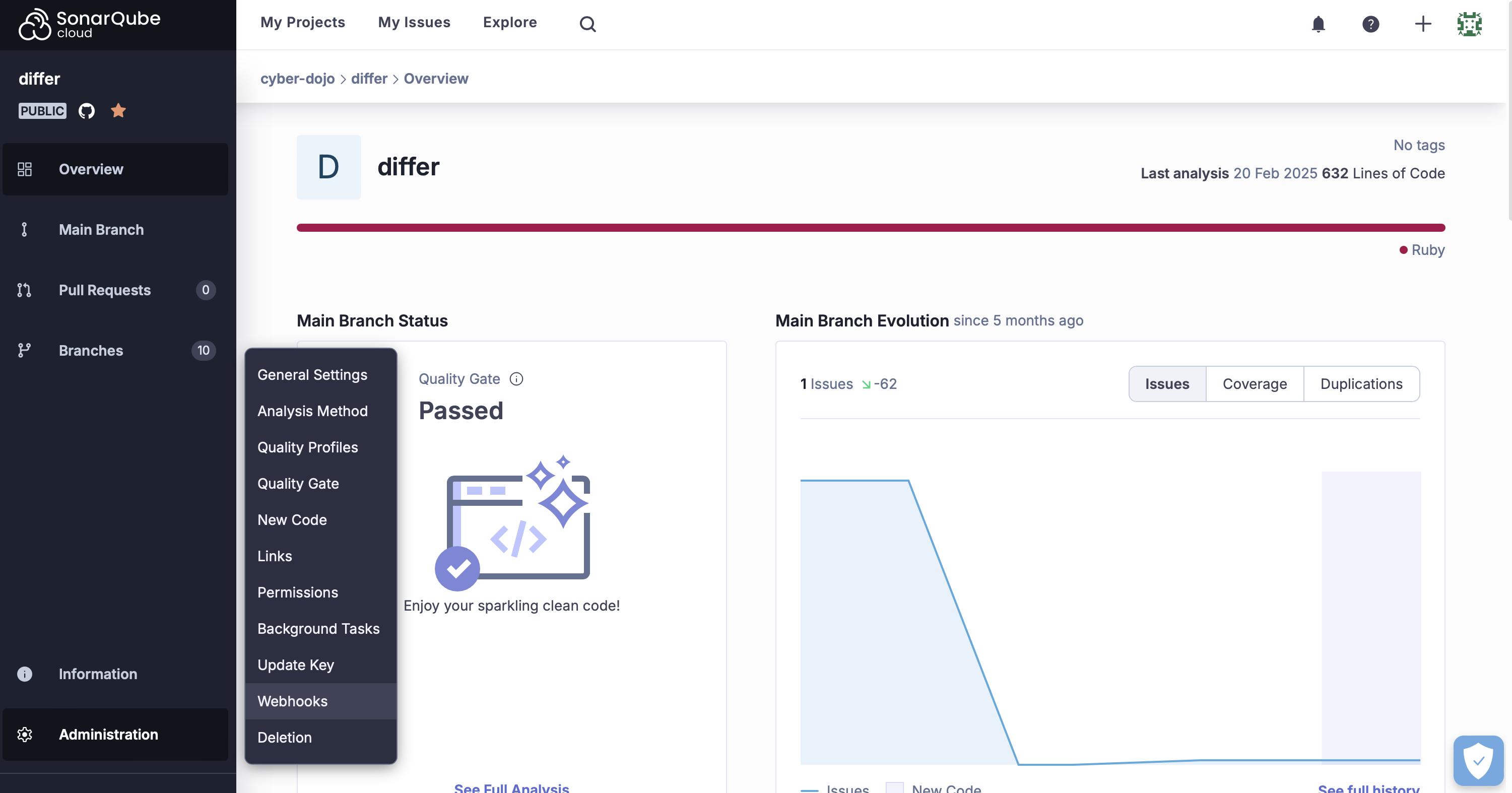
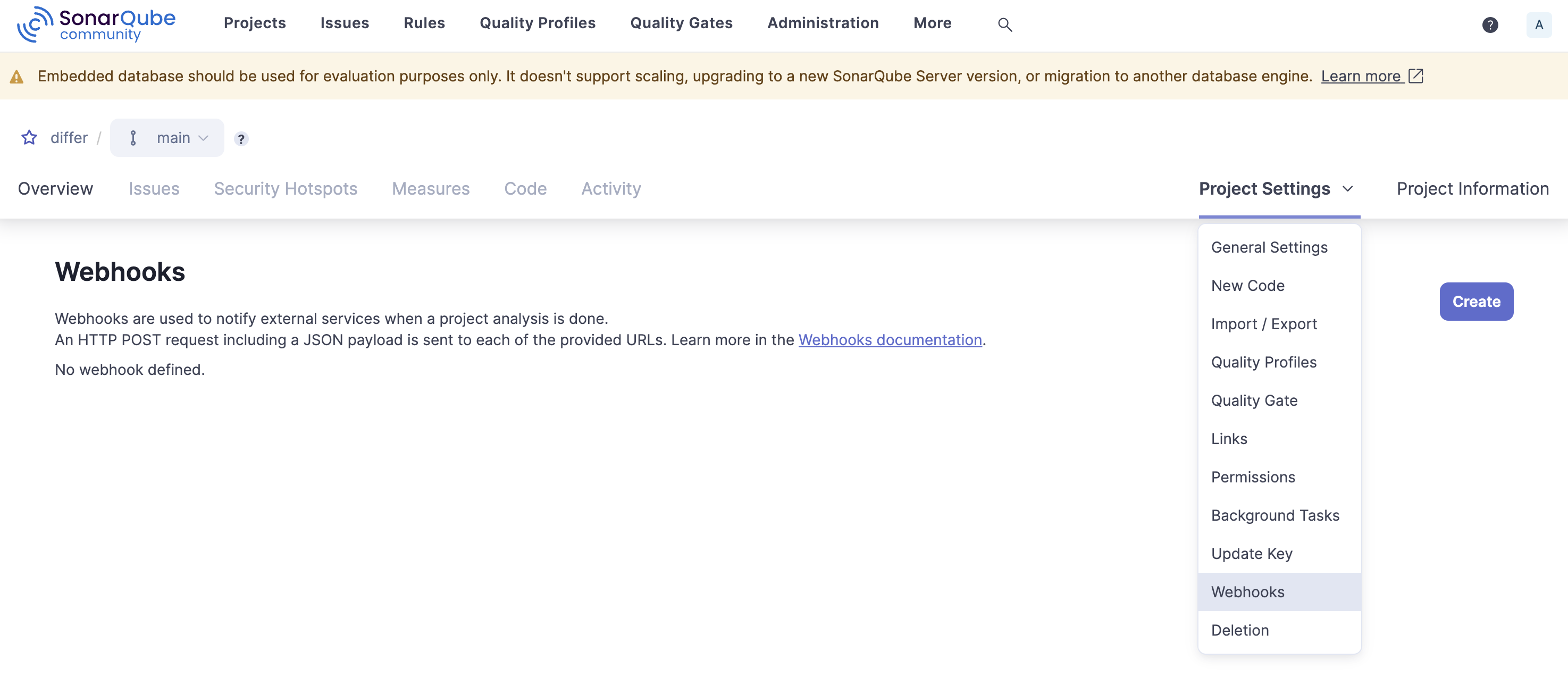
To create a project-specific webhook: #
- Go to the project you want to create a webhook for
- Click on Administration (SonarQube Cloud) or Project Settings (SonarQube Server) and go to Webhooks in the dropdown menu
- Create a new Webhook
- Add the Kosli webhook URL and secret provided
- Click Create
Setting up the SonarScanner #
In order for Kosli to know where the scan results should be attested, certain parameters can be passed to the SonarScanner. Note that parameters cannot be passed with SonarQube Cloud's Automatic Analysis - in this case, Kosli determines the relevant Flow and Trail as described below.
These parameters can be passed to the scanner in three ways:
- As part of the sonar-project.properties file used in CI analysis
- As arguments to the scanner in your CI pipeline's YML file
- name: SonarQube Scan
uses: SonarSource/sonarqube-scan-action@master
with:
args: >
-Dsonar.analysis.kosli_flow=<YourFlowName>
-Dsonar.analysis.kosli_trail=<YourTrailName>
- As arguments to the CLI scanner
$ sonar-scanner \
-Dsonar.analysis.kosli_flow=<YourFlowName> \
-Dsonar.analysis.kosli_trail=<YourTrailName>
Scanner parameters: #
sonar.analysis.kosli_flow=<YourFlowName>- The name of the Flow relevant to your project. If a Flow does not already exist with the given name, it is created. If no Flow name is provided, it is determined using the chosen Flow name configuration (see Configuring the flow name above), with any invalid symbols replaced by '-'.
sonar.analysis.kosli_trail=<YourTrailName>- The name of the Trail to attest the scan results. If a Trail does not already exist with the given name it is created. If no Trail name is provided, the revision ID of the SonarQube project (typically defaulted to the Git SHA) is used as the name.
sonar.analysis.kosli_attestation=<YourAttestationName>- The name you want to give to the attestation. If not provided, a default name "sonar" is used. If using dot-notation (of the form
<YourTargetArtifact.YourAttestationName>), either the artifact fingerprint or git commit is also required (see below).
- The name you want to give to the attestation. If not provided, a default name "sonar" is used. If using dot-notation (of the form
sonar.analysis.kosli_git_commit=<GitCommitSHA>- The git commit for the attestation. If not provided the revision ID of the SonarQube project is used (provided it has the correct format for a git SHA).
sonar.analysis.kosli_artifact_fingerprint=<YourArtifactFingerprint>- The fingerprint of the artifact you want the attestation to be attached to. Requires that the artifact has already been reported to Kosli.
sonar.analysis.kosli_flow_description=<DescriptionOfYourKosliFlow>- The description for the Kosli Flow being created by this webhook. This will not be used if attesting to an already-existing Flow (i.e. will not change any existing descriptions).
sonar.analysis.kosli_trail_description=<DescriptionOfYourKosliTrail>- The description for the Kosli Trail being created by this webhook. This will not be used if attesting to an already-existing Trail (i.e. will not change any existing descriptions).
Testing the integration #
To test the webhook once configured, simply scan a project in SonarQube. If successful, the results of the scan will be attested to the relevant Flow and Trail (and artifact, if applicable) as a sonar attestation.
If the webhook fails, check that you have passed the parameters to the scanner correctly, and that the trail name, attestation name and artifact fingerprint are valid.
Live Example in CI system #
View an example of a sonar attestation via webhook in Github.
In this YAML file, which created this Kosli event.
Alternatives: #
If you'd rather not use webhooks, or they don't quite fit your use-case, we also have a CLI command for attesting Sonar scan results to Kosli.